Building a basic DIY off-grid solar power systems is a fun, challenging, and worthwhile journey to make. It is fun since you will enjoy every single step of creating an off-grid system by yourself. This journey can be challenging, too, since it will require a considerable amount of your time, skills, and effort to make the project a reality.
Building a DIY off-grid solar power systems is worthwhile. It will not only make you learn more about solar energy, but also, it will add more value to you as an individual in return. So, why not start learning now and build your off-grid system the soonest.

What is an Off-Grid Solar System?
An off-grid solar system is a stand-alone electrical power system that uses solar energy as its resource.
An off-grid solar system is not connected to the main public utilities (especially the electricity grid).It generates DC electricity from solar panels and stores it by utilizing batteries. It powers the home appliances by converting the stored DC electricity into AC using an off-grid inverter.
Furthermore, we will give you a simple explanation of what an off-grid solar power system is. Some articles and books talk about this topic but, they can be confusing sometimes. The main goal is to give you a strong start for your DIY off-grid solar power systems project.
Typical Off-Grid Solar Power Systems Diagram
Here, you will see a couple of wiring diagrams for a typical off-grid solar system. A wiring diagram, by the way, is a simple depiction of how each component of a system is connected. Typically, an off-grid solar power system includes solar modules, DC cables, a battery, a charge controller, and a battery inverter.
What does Off-Grid mean?
The first part, which is off-grid, means being independent of the common electrical grid. In other words, it means moving away and being disconnected from the utility pole, transformer, or substation that the energy utility owns.
Going off-the-grid means supplying your own electricity source instead of getting it from the public power grid. It also means generating electricity to power home appliances, lighting, and other electrical equipment using an alternative source.
What is a Solar PV System?
The second part, the ‘solar PV system’ or solar photovoltaic system, means an electrical network that uses solar energy to supply electrical power. In simple terms, this is a power plant that only uses sunlight as its primary resource. It is mainly composed of solar modules, charge controllers, batteries, and electrical loads.
Thus, an off-grid solar system refers to a system that works without the support of traditional public utility services. It meets the electricity needs of the house, plant, or facility using the energy coming from the Sun.
Usually, this type of system can be accompanied by batteries or a backup generator to provide power during the night.
How does an Off-Grid System Work?
Ideally, the loads will be powered by solar panels during the day. When the sun goes down, the batteries will take over and supply electricity to the home appliances. The battery system should be large enough to provide power throughout the night. Solar panels will then charge them during the day while supplying power to the loads This is how an off-grid solar power system is expected to work.
The system generates DC electricity from the solar panels during the day. This process involves the photovoltaic (PV) effect within solar panels and rays of light coming from the Sun.
As sunlight hits the surface of solar cells, electrons become free and excited. This allows them to flow through the solar panel’s cables as direct current electricity.
Depending on the system setup, the direct current can directly go to an inverter where the electricity is converted to AC or alternating current. This will then become the electricity that the appliances use.
Off-Grid Energy Storage
There will be instances where solar energy production is more than the energy consumption of the appliances. During this time, the battery system stores any excess or extra electricity.
The energy stored in the battery provides electricity to the appliances when the PV system cannot produce the desired amount of electricity. This happens during the night or on cloudy days.
Optional Backup Generator
Sometimes, you need to counter the low electricity production due to poor weather conditions. In this situation, a backup generator can also be taken into consideration. It can provide a power supply to the house and charge the batteries simultaneously when necessary.
A backup generator comes in handy when the battery system runs low on energy. This mostly happens when the energy storage system discharges for an extended period of time without being charged by the solar PV system. During these instances, the backup generator will supply your electrical needs. It can even work in parallel with your solar panels in charging the batteries.
DIY Off-Grid Solar Power System Components
To start well, you need to know which materials you will need to prepare. By learning and understanding the essential solar off-grid items, you will have an incredible take-off on your DIY journey. Now, an off-grid solar system requires the following extra components for its effective operation.
1. Solar Panels
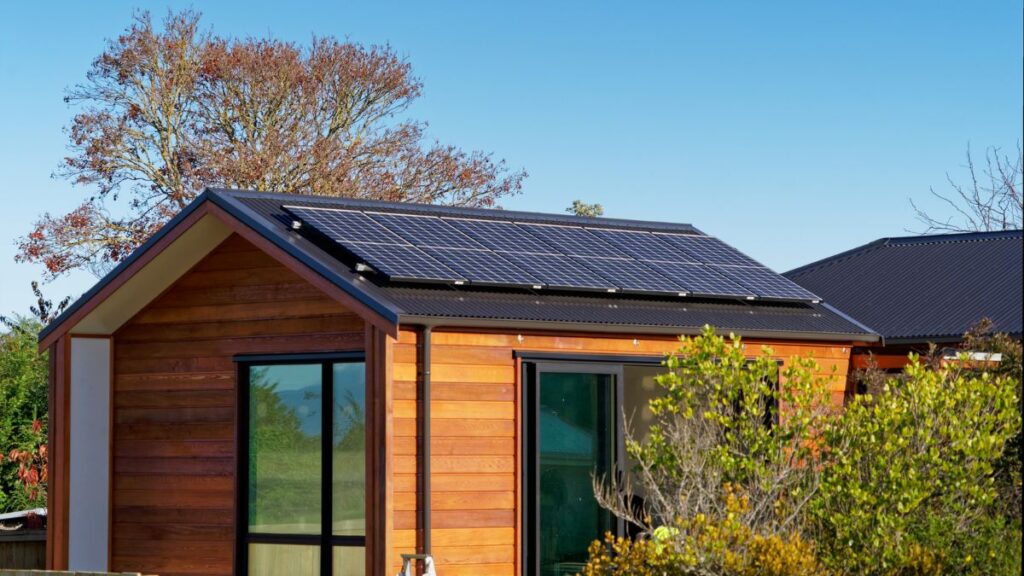

A photovoltaic solar panel is a device that produces electrical energy by absorbing sunlight and transforming it into direct current electricity. This is further explained in our post about solar panels for homes, where it discusses the different types, attributes, and uses of solar panels.
In an off-grid solar power system, you can install the panels on the roof or the ground along with their mounting supports. If you are an avid fan of RV’s or boats, you will most likely be interested in installing solar panels with an off-grid configuration.
2. Solar Charge Controller

A solar charge controller, also known as a charge regulator, is simply a voltage and current regulator for battery charging purposes. It means it controls how your batteries are charged and keeps them from overheating. Charge controllers protect the energy storage system from any damages due to over-voltage or over-current from the solar energy sources.
- We use charge controllers to regulate the voltage and current going to the battery.
- Solar panels will have various voltage levels as an output, ranging from 12 Vdc to 80 Vdc.
- So if there is no means of regulating the voltages, the batteries can be damaged when solar panels are overcharging them.
To protect your energy storage system and prolong battery life, you will need to install a solar charge controller.
3. Battery or Energy Storage System
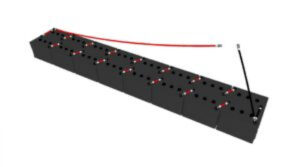
An energy storage system is made up of one or more batteries depending on your requirements. Its primary purpose is to store up electrical energy, mostly from solar or other renewable energy supply, for later use. When you connect two or more batteries, it can now be called a battery bank. This is widely used in off-grid systems.
The battery bank is usually connected to 3 other systems. This includes renewable energy sources (i.e., solar panels, wind turbines, etc.), backup generators, and electrical loads (i.e., AC and DC appliances).
4. DC Disconnect Switch

DC disconnect switches are usually placed in between solar panels, charge controllers, and batteries. It will stop the current flowing between these devices when necessary, such as during maintenance, upgrading, or repairing the system. Hence, the component plays a vital role in making the whole system safe and easy to maintain.
5. Off-Grid Inverter

To utilize solar energy, an off-grid inverter is needed to power your home appliances. This is considered the “heart/brain” of the off-grid solar system. The input side of the inverter will require the wiring connection from the charge controller to it. It takes direct current or DC.
The output side of a typical off-grid inverter connects to the AC loads or the main panel where your appliances are connected. The inverter converts the DC electricity that the solar panels or the battery supplies to AC electricity.
6. Backup Generator
There are times when the off-grid solar power systems cannot produce electricity over a period of time due to cloudy weather. In this scenario, the backup generator comes into the picture. The generator will temporarily supply the necessary power to operate the electrical loads.
Usually, this happens when procuring huge-sized batteries becomes more expensive than having a backup generator. To prepare for several days without electricity production from the solar panels, the generator will fill the gap. It can even charge the battery bank if it is necessary.

Steps in Designing Off-Grid Solar Systems
Building an off-grid solar power system by yourself means you have to design it as well. Making a plan beforehand will help in the successful installation of your DIY off-grid system. Assuredly, this project will be a great success when you design it correctly and implement it accordingly. Here are the things you need to know to do when planning your off-grid solar system.
Step 1: Load and Power Consumption Calculation
First, you will need to calculate your power consumption according to your daily requirements. This means you need to determine how much electrical energy you consume using your home appliances each day. The more accurate you are on this, the better the design you can create.
Know the Power Requirement of Your Home
Knowing the individual power requirement of your appliances or equipment is essential in this stage. It is helpful if you list down all your devices with their corresponding power requirements in Watts. You may usually see this on their information nameplates. This is a crucial step to do so that you will not fall short or oversize your off-grid solar system capacity.
Before choosing the components, you have to calculate your power consumption. How long are you planning to run your appliances in hours? What is the individual load requirement of your devices in Watts? To calculate the power consumption in Watt-hours, simply answer the questions and multiply each load (Watts) by the time (hours) they need to be running.
- Plan what appliances (light, fan, TV, etc.) you want to run. Write down how long you want each of them to run, in hours.
- Check the nameplate or your appliances for power rating.
- Calculate the Watt Hour, which is equal to the product of the power rating of your appliances and run time (hours).
Load Calculation Example:
Let’s say you want to run an 11W compact fluorescent lamp (CFL) for 6 hours; then the watt-hour will be equal to:
Watt-Hour = 11W x 6 hr = 66 Wh
Calculate the total Watt Hour: Just as with the CFL, we’ll now calculate the Watt-hour for all the appliances and add them together.
So by now, we already know how much your average electricity consumption is daily. You will need this information to have a proper sizing of the batteries. And that will be our next step.
Step 2: Battery sizing and selection
Once you have your load calculation, you may now then calculate the size of the battery you will need. Here are some of the factors you need to consider when selecting the size of your energy storage system or battery bank:
Factors to Be Considered
- Days of Autonomy. This refers to the days the energy storage will still be enough without charging the batteries, during cloudy days or days without enough sunlight.
- Depth of Discharge. This refers to “the fraction or percentage of the capacity which has been removed from the fully charged battery. It is an alternative method to indicate a battery’s State of Charge (SoC)” – source.
- Battery System Voltage. This will depend on the DC voltage requirements of your appliances or equipment you want to use.
- Charge Controller Efficiency. This will determine the losses of energy due to the internal circuitry of the charge controller. Most of the charge controllers nowadays have a maximum efficiency between 90 to 98%.
- Amp-hour Rating. “An ampere-hour or amp-hour (symbol:
A⋅h or Ah; often also unofficially denoted as Ah) is a unit of electric charge, having dimensions of electric current multiplied by time, equal to the charge transferred by a steady current of one ampere flowing for one hour, or 3,600 coulombs.” – source.
All the factors mentioned above will be important in sizing the battery for your off-grid system.
Example Battery Sizing Calculation
For example, to properly size the battery bank, we have determined the following factors:
- Days of Autonomy = 2 days
- Depth of Discharge = 80%
- Battery System Voltage = 24 V
- Charge Controller Efficiency= 90%
- Daily Consumption = 556 Watt-hours
When calculating the battery size of our energy storage system, we need to know the Ah or Amp-hour rating of the battery first. So, let’s do the calculation.
- Ah Rating = (Daily Consumption/Battery System Voltage) x Days of Autonomy/Depth of Discharge/C. C. Efficiency
- Ah Rating = (556 Watt-hours / 24 V) x 2 / 0.80 / 0.90
- Ah Rating = (23.17 Ah) x 2 / 0.80 / 0.90
- Ah Rating = 64.35 Ah or 1.544 kWh (@24V DC)
Therefore, you will need at least a 65-Ah battery with 24V DC Voltage or two units of 65-Ah batteries with 12V DC to satisfy your daily electricity consumption with those three appliances.
Step 3: Solar panel sizing
What are the things to consider when sizing solar panels for an off-grid system? When sizing your solar panels, you need to consider the following:
- Average Sun Hours in your Area.
- Maximum Power Capacity of your Solar Panels.
- Available Usable Area for your Solar Panels.
Average Sun Hours
The average sun hours or peak hours in your area will determine how much solar energy you can potentially produce using your solar panels. Most sunny places will enjoy around 4 to 6 hours of sunlight each day. These places will be the ones that will benefit the most.
Now, if you’re in a place not so blessed with sunlight, don’t worry, as you can still generate the solar energy needed. You have to install a more extensive and more efficient solar panel system.
To size your solar panels, you need to know your battery capacity and your load first. Once you have those values, you will see that your solar panels can charge your batteries to the full capacity during the day. This will determine the charging cycle of your battery as it discharges during the night to supply your load.
Maximum Power Output of Solar Panels
To determine how many solar panels you need to achieve the overall power capacity of your desired system, you need to know the solar panel’s maximum power output.
For example, if you require a 5-kilowatt solar panel system, you have to calculate the number of modules based on their individual capacity. Let’s say you choose the 545-Watt modules in the market now so that you will need at least ten units of these. This will give you a 5.45-kilowatt-peak or 5.4 kWp solar power system.
Determine Usable Areas for Solar Panels
You can install your solar panels on the roof, ground area, or even on your carport. It is also essential to know what areas in your home are available for solar panel installation.
The number of solar modules you can have for your off-grid system will be determined by this as well. When you know the dimensions of the places you want to install solar panels, you can estimate the maximum size of the system.
For example, suppose you have an area of 50 sq. m. on your roof, knowing that solar panels would be approximately 1 meter by 2 meters in dimension. In that case, you can install at most 24 solar modules in that specific area.
Example Solar Panel Sizing Calculation
If we consider the details on the previous example, we will have the following things to consider:
- Energy Storage Capacity: 1.544 kWh or 1,544 Watt-hours
- Average Sun Hours: 5 hours
- Charge Controller Efficiency: 90%
Solar Panel Capacity = Energy Storage Capacity / Average Sun Hours / Charge Controller Efficiency
Solar Panel Capacity = 1,544 Watt-hours / 5 hours / 0.90
Solar Panel Capacity = 343 Watts
Recommended Solar Panel Capacity = at least 400 Watts
So, you will need at least 400 Watts of solar panels for you to have enough energy in your batteries. It can be a 400Wp module or two units of 200Wp modules or four 100Wp modules. Depending on the availability, your choice can be flexible for this system.
Step 4: Charge controller selection
When selecting your charge controller, you need to know the following:
- The maximum current of the batteries.
- Solar panels total power output.
- Voltage level requirement of the loads or home appliances.
Select the solar charge controller based on your solar panels and battery’s current rating, DC voltage, and power capacity. Always make sure to check the model specifications to size it correctly.
Step 5: Cable and breaker sizing
Always refer to the electrical equipment standards when doing the sizing of cables and breakers. You will have to do the sizing exercise for both the AC and DC parts of the system.
Step 6: Choosing the right mounting structure
When choosing the mounting structure, you have to establish first where you want to fix your solar panels.
There are many types of solar panel mounting structures, but the most common ones are the following:
- Sloped Roof Mounting Structures
- Flat Roof Mounting Structures
- Ground-Mounted Structures
- Ballasted Type Mounting Structures
Each of them has unique forms and structures based on the application.
Always make sure that you follow the installation manual when installing them. Mainly, it will be composed of rigid and metallic materials like aluminum, stainless steel, or galvanized iron.

What Tools Do I Need When Installing Off-Grid Systems?
To start with building your DIY off-grid system, you need to prepare the following tools. Make sure that you also have your safety equipment and PPE before beginning the installation.
- Safety should always be the priority!
- Cable Crimping Tool
- Cable Cutter
- Cordless Drill
- Screw Drivers
- Power Drill
- Bolt and Nut Driver Tools
- Allen Keys
- Measuring Tape
- Hole Saw Cutter
- AC/DC Multimeter
- Pliers
- Ladders
- Fall-Arrests
- Personal Protective Equipment
Steps in Building the DIY Off-Grid Solar Power Systems
After you have done designing your system, it is now time to build it. By following the simple steps below, you will make an off-grid solar PV system on your own.
Step 1: Start with the mounting structures
The first thing to do once you have all the tools and materials for your off-grid solar system is to build the mounting structures.
It might involve climbing to your roof and fixing the mounting rails. Or, it may include making the foundations first if you intend to install it in the ground or on a flat roof.
Once you secure all the structures and railings, ensure that you maintain proper distances between them. This will create a suitable maintenance path or even avoid unnecessary shading between solar panels.
Additionally, make sure that you have provisions for the grounding cables to have a proper earthing connection.
Step 2: Install the solar panels on the mounting structures securely
Start to fix the solar panels into the railings of the structures. Do it one by one in a safe manner. Fix each of the modules in place using the end and mid clamps.
Step 3: Do the interconnection of solar panels correctly
Connect the solar panels in series as per your design.
Step 4: Fix and connect the DC cables safely
Lay down the cables with their containment system. You can use cable trays, cable trunks, or conduits. Each end of the wires should be crimped and fixed with MC4 connectors.
Having red cables for the positive and black wires for the negative is an excellent practice when installing a solar power system. Make sure you adhere to this to avoid confusion on the cable termination. Always put cable tags for every cable ends.
Step 5: Install the solar charge controller or off-grid inverter
Fix the solar charge controller and off-grid inverter in a secured place. There will be DC cables connecting to the solar panels and the batteries. Always make sure that safety precautions are observed at all times.
Step 6: Make sure to install the AC and DC breakers properly
Install the AC and DC breakers. Use the proper tools and PPE when fixing these units.
Step 7: Install the battery in a safe manner
Make sure to install the batteries in a dry and secure place. As much as possible, always connect cables for the positive and negative terminals in the same length. This will avoid any unbalanced current flow, and this is also considered a good and safe practice.
Step 8: Connect the off-grid inverter to the load
Once all of the DC cables are installed, you can start fixing the AC cable from the off-grid inverter to the load. This means you will connect the inverter’s output side into the allocated breaker in the electrical distribution board of your property.
Step 9: Testing and Commissioning
Check all the values of insulation for all the cables. Use proper measuring equipment and record every value for safekeeping. Also, check the continuity of the grounding cables to the structures, module frames, an earth pit. This will ensure that there will be no dangerous leakage current that can cause harm to anyone.
Start commissioning the inverter and charge controllers. Make sure all the values for the voltage, current, and power are as what is expected. If there are any abnormalities on the values, make sure to find where the fault is and do not operate the system unless everything is cleared out.
Why Do People Go Off-Grid Living?
There are a lot of reasons why people opt for off-grid living. The list includes being practical, living a life with less carbon footprint, using renewable energy, and the list goes on.
Where Can We See Off-Grid Solar Power Systems?
Since off-grid systems are independent of the grid, they are most commonly used in remote areas. These are places where there is an unreliable utility service. It can also include areas where grid electricity is costly to consume or where there is no available power grid at all.
However, we can also see this type of system in urban places. People who usually opt for this type of energy source have different reasons why they build it. It ranges from being a hobbyist, exploring solar energy, and powering special appliances or devices with sunlight.
Bottom Line for DIY Off-Grid Solar Power Systems
Despite their advantages, batteries and generators can provide a finite amount of electrical power. Hence, power conservation is necessary to make an off-grid system perform as expected. Power conservation becomes achievable by choosing the right appliances and adopting energy-efficient habits such as proper sizing of energy demands, adequate wiring, etc.
You need to design and implement your DIY off-grid system effectively and correctly. By doing so, the result will be a fully functioning renewable power system that you can be proud of.




